Introduction to CO-PA:
- Basically, COPA will be used to evaluate the “Profitability” of an organization according to their business units and it also captures the various details like discounts, expenses & promotions to obtain the actual profit details.
- COPA helps the organization to compare the plan & actual sales, so that we can analyze the performance of various business units and if requires we can take necessary actions accordingly.
- Organizations can also submit their different forecasts or targets for various organizational units for various periods in CO-PA.
Types of Profitability Analysis
We have 2 types of Profitability Analysis in COPA:
- Costing-based Profitability. is the form of profitability analysis that groups costs and revenues according to value fields and costing-based valuation approaches.
This type of Profitability Analysis is primarily designed to let you analyze profit quickly for the purpose of sales management. Its main features are, firstly, the use of value fields to group cost and revenue elements, and, secondly, automatic calculation of anticipated or accrual data (valuation). The advantage of this method is that data is always up-to-date and therefore provides an effective instrument for controlling sales.
- Account-based Profitability. is a form of profitability analysis organized in accounts and using an account based valuation approach.
This type of Profitability Analysis enables you to reconcile cost and financial accounting at any time using accounts. In contrast to costing-based Profitability Analysis, this type uses cost and revenue elements, which gives you a unified structure for all of accounting.
The system posts all revenues and costs to both Financial Accounting and Profitability Analysis at the same time and using the same valuation method. This means that the cost of sales is posted to Profitability Analysis at the point of goods issue.
What is Operating Concern?
Operating concern which constitutes, combination of characteristics (Customer, Product, Company, Controlling, Controlling Area, etc) & Value fields (Sales Qty, Gross sales, Discounts, Expenses, Net sales, Trade Promotions, Coupons etc) to analyze its profitability.
Characteristics:
Characteristics are the criteria in Profitability Analysis (CO.PA) according to which you can analyze your operating results and perform differentiated sales and profit planning.
You create characteristics in Customizing under Structures _ Operating Concern _ Maintain
Characteristics.
Value fields:
Value fields are only required in costing-based Profitability Analysis. These are the fields that contain the currency amounts and quantities that you want to analyze in CO.PA. They
represent the structure of your costs and revenues. You create Value fields in Customizing under Structures _ Operating Concern _ Maintain Value fields.
Prerequisites for creating OC:
- Create Company Code (SPRO->Enterprise Structure-> Definition-> financial accounting-> check company code).
- Create Controlling area (SPRO->Enterprise Structure-> Definition-> Controlling-> Maintain controlling area).
- Crate Operating concern in KEA0.
- Creation of Cost Element Group in KAH1
- Assign the cost element group under a value field in KEI2
- Assign Company code to Controlling area in T-code OX19.
- Assign Controlling area to Operating Concern in T-code KEKK.
Note: All the above settings were maintained by FI Consultants.
About CO-PA Data source:
Basically for CO-PA, no standard SAP delivered data sources are available, CO-PA is totally client specific, means based on the client requirement we are going to create CO-PA data source on the client specified operating concern (Specified Characteristics & Value fields)
- Transaction to create CO-PA Data source - KEBO
- CO-PA Data source name should start with 1_CO_PA<XXXX> (i.e. XXXX=Your Description) ,name can be maximum of 19 character length
- Custom Characteristics name should be started with WW<XXXX> and value fields name should be started with VV<XXX>, where “XXX” our own description
- For each CO-PA specific field with a name consisting of five characters, the system generates a corresponding Info object in the back ground. The name of the Info object generated consists of the field name (five characters) with the prefix 0G_x, whereby x=C for characteristic, X=A for amount, X=Q for quantity, and X=U for unit of measure In this way, Info object 0G_CWW001 is generated for characteristic WW001
- As in BI 7.0 version we are no longer using Info source, we can first replicate the CO-PA data sources as 3.x data source, to create the info objects for custom characteristics and value fields automatically. Then we can delete that data source from BW and replicate as 7.0 data source. All info objects will be remain there in the system
- CO-PA data source cannot be enhanced. If we have to add/delete fields from data source operating concern has to be modified with the addition/deletion of fiels. Now that new field cannot be adjusted with the existing data source. Data source has to be deleted and recreated.
- If you created the data source with the same as old data source name, no need to create transformations in BW newly. We have to replicate the new data source and transformations/DTPs have to be re-activated.
Database Tables used for CO-PA Model:
The CO-PA Model is basically based on following 4 tables
CE1XXXX, CE2XXXX, CE3XXXX and CE4XXXX – Here “XXXX” denotes operating concern, specific to organization.
CE1XXXX: This Table contains Actual transaction data in detail level. Daily transactions, Invoices are captured in this table.
CE2XXXX: This Table contains Plan/Target line item data. All planned data, different estimates are stored in this table.
CE3XXXX: This table holds Segment level data. This is set up between the segment table and the line items.
CE4XXXX: This is the segment table, which is located at a higher level. It is used to assign segment numbers to each combination of characteristic values.
Note1: When this CO-PA data is getting extracted in BW in delta mode data is always read from Line item tables (CE1 or CE2).
Note2: An extraction from the segment level, that is, from the combination of the tables CE3/CE4, is only performed for Full Updates if no line item characteristics are selected.
Steps To Create Operating Concern:
Go to transaction SPRO, Controlling.> Profitability analysis .> Structures .> Define Operating Concern .> Maintain Operating Concern. Or KEA0 is the direct T-code.
Step 1: Go to T-code KEA0, choose create, specify the OC, description and select type of PA and Save.
Step 2: After saving we have to maintain the Data Structure, Click on the change button.
Step 3: Assign the required characteristics to data structure.
Step 4: Assign the required value fields to data structure.
Check, Save, Activate and go back.
Step 5: Go to “Attributes Tab” Provide required “Operating concern Currency & Fiscal year variant”.
Step 6: Go to “Environment Tab” in order to make operating concern active, Press Activate.
Operating Concern Activated Successfully.
Note: Once the Operating concern is created, these tables CE1XXXX, CE2XXXX, CE3XXXX and CE4XXXX are created automatically in the back-end which can be seen in SE11.
Database Tables used for CO-PA Model:
The CO-PA Model is basically based on following 4 tables (once the Operating concern is created, these tables are created automatically).
CE1XXXX, CE2XXXX, CE3XXXX and CE4XXXX – Here “XXXX” denotes operating concern, specific to organization.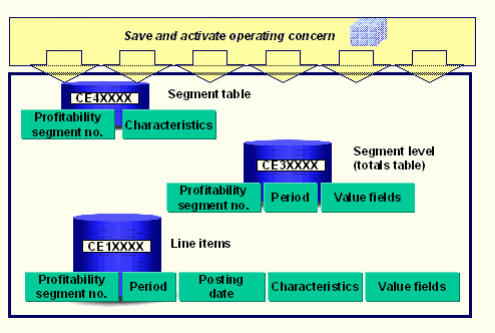
CE1XXXX: This Table contains Actual transaction data in detail level. Daily transactions, Invoices are captured in this table.
CE2XXXX: This Table contains Plan/Target line item data. All planned data, different estimates are stored in this table.
CE3XXXX: This table holds Segment level data. This is set up between the segment table and the line items.
CE4XXXX: This is the segment table, which is located at a higher level. It is used to assign segment numbers to each combination of characteristic values.
So, when the line items (CE1 & CE2) are posted, the segment table (CE4) and segment level (CE3) is updated.
About CO-PA Data source: ( BW Steps Going to Start )
Basically for CO-PA, no standard SAP delivered data sources are available, CO-PA is totally client specific, means based on the client requirement we are going to create CO.PA data source on the client specified operating concern (Specified Characteristics & Value fields).
- Transaction to create CO-PA Data source - KEBO
- CO-PA Data source name should start with 1_CO_PA<XXXX> (i.e. XXXX=Your Description) ,name can be maximum of 19 character length
- CO-PA data source cannot be enhanced. If we have to add/delete fields from data source operating concern has to be modified with the addition/deletion of fields.
Creation of Data Source:
Steps in R/3:
Step1: Go to T-code KEB0 and specify the Data source name, choose the Create function, provide the relevant operating concern, and select Cos-based accounting.
Step 2: Provide Short, Medium and long descriptions. Specify the field name for partitioning and double click on that field to initialize.
Check for consistency of data (ctrl + F2) and give F7 to create Data source
Step 3: Save the data source & go back
Steps in BW side:
Step 1: Replicate Data source in RSA1.
Check & Activate.
Step 2: Create & Schedule the Info package.
Step 3: Create Transformations.
Step 4: Create DTP & Execute.
Step6: Check the data in the Info cube.
Delta Mechanism:
The following diagram is illustrating how the delta mechanism in CO.PA
Some points to be noted regarding Delta:
- When this CO.PA data is getting extracted in BW in delta mode data is always read from Line item tables (CE1 or CE2).
- An extraction from the segment level, that is, from the combination of the tables CE3/CE4, is only performed for Full Updates if no line item characteristics are selected.
- Generic Delta in COPA is based on Time stamp, while creating CO.PA data source it will be generated automatically.
- Once the' INIT' is successful, you will have to maintain minimum of 1/2 hrs time before you schedule the delta load (This is called “safety delta”).
- Half an hour was chosen as the safety delta to overcome any time differences between the clocks on the different application servers.
- Doesn’t use the delta queue. CO-PA delta is based on timestamp, which is updated after each delta extraction & reads delta from the CO-PA tables directly.
Transaction codes in CO-PA:
T-code
|
Description
|
SPRO
| |
KEA0
|
Maintain Operating Concern
|
OX19
|
Assigning company code to controlling area
|
KEKK
|
Assigning Controlling area to Operating Concern
|
Kei2
|
PA Transfer Structure
|
KAH3
|
Cost element Display
|
KAH1
|
Creation of Cost element
|
KEB0
|
Creation of Data Source
|
KEB2
|
Display Detailed information about Data Source
|
KECP
|
TO Copy OC or Spro -> Controlling -> PA-> structures-> Defind OC ->sample oc->copy oc
|
KEB5
|
To check the TimeStamp
|
Points to remember :
CO-PA Extraction:
-------------------
- it comes as part of custom generated extractors
- Operating Concern
- CO-PA is an integration module
- why No business content....?
- 4 tables [CE1XXXX,CE2XXXX,CE3XXXX,CE4XXXX]
- CE1XXXX - aCTUAL DATA
- CE2XXXX - PLAN DATA
- CE3XXXX - sEGMENT TABLE
- CE4XXXX - SEGMENT LEVEL TABLE
- Value Type
- Version
- Currency Type
- Steps how to generate the data source for CO-PA?
-------------------------------------------------
VV140 --- 0G_AVV140
-Delta Mechanism:
-----------------
- Timestamp (yyyymmddhhmmss)
- KEB2
- KEB5 (Realignment of Timestamp)
- Delta Process:
----------------
ROOSOURCE --- RODELTAM
- Reconcilation
---------------
-KE30
-------------------------------------------------
Delta Pointer - In RSA7
First time: “Init With Data Transfer” was done (Because of this, if you see in the below second screen shot the Delta update was initialized/became enable.
To see whether the delta pointer is enabled or not
Note: “Initialization Options for Source System” -- > it is to just check whether the delta pointer was set in RSA7 or not,,, and also if you want to delete that “Delta Pointer” in RSA7, from here (means from BW side), you can also delete.
RSA7: To cross check at R/3 side(To see whether the delta pointer is enabled or not)
Click on the below “Pointer for Generic Delta” Icon -→ To see exactly, where the delta pointer was set, I mean on which record the pointer was set(it is when you maintain delta field in the generic data source) or at what point of time the delta pointer set(if you maintain the delta field as any Time Characteristic)
Here, they have maintained “Delta field” as ZVBELN (Sales Document Number), so full load was happened till the sales document number “905”. Means the delta pointer was set at 905 sales doc number, suppose if you start the next delta run, by that the system will the records from the sales document number 906 on words.
To cross verify, check in the “Datasource records & Info cube records”, whether the sales documents number till 905 was transferred or not.
Infocube records.
Checking the Generic Delta Field (Field Num), in RSO2 at R/3 side (in Generic Datasource)
Check the below “Delta field” as “ZVBELN” and also one more point, we are doing this extraction based on Table, that is the reason why we have selected “Numeric Pointer” as Delta type.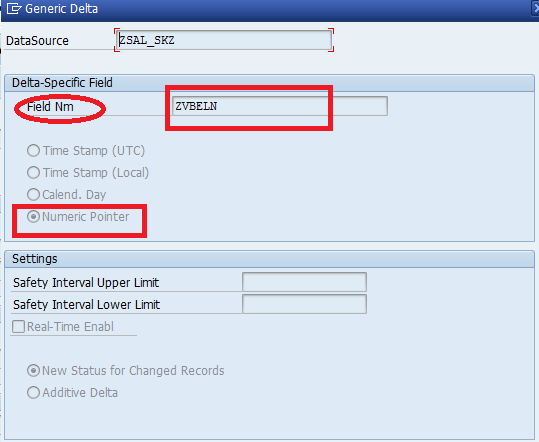
Another Generic Delta Scenario with the Delta field type as Time Characteristic and Delta Type as Time Stamp.
“Delta Field (Field Num)” as Time Characteristic ( Delta Type as “Time Stamp” --- Though we are doing Table extraction we haven’t went for Numeric Pointer Delta type,,, bcz here the Delta Field (Field Num) we have given Time characteristic,, that is the reason why we selected Delta type as “Time Stamp”
So final conclusion is your type of “Delta type” you are going to select based on the field which you are going to give / select in that “Field Num” Delta field.
RSA7:
In the above it is Showing the time stamp of last load when it was started,
Why it is showing Time showing as Delta pointer???
It is bcz of we have maintained Time characteristic(Zfiscper) as Generic Delta Field in Generic Datasource at RSO2,, you can check that in below.
====================================================================
COPA EXTRACTION STEPS
Differences between COPA delta and LO delta
The Logistics extraction and other extractions like FI, and COPA have a different extraction technology.
In LO extraction, the setup reads the dataset that you want to process such as, customer orders with the application tables VBAK, VBAP.. and fill the relevant communication structures with data. The data is stored in cluster tables from where it is read when the initialization is run.
Where as the other extractions like FI,CO-PA.. Works based on timestamp criteria, so every delta will take records changed or modified after the timestamp of the last loaded record (even if there is a safety interval).
Also One of the main difference is that the CO/FI data sources are "pull based", meaning, that the delta mechanism is based on a time stamp in the source table and data is pulled from these tables into the RSA7 queue.
In LO extraction, the setup reads the dataset that you want to process such as, customer orders with the application tables VBAK, VBAP.. and fill the relevant communication structures with data. The data is stored in cluster tables from where it is read when the initialization is run.
Where as the other extractions like FI,CO-PA.. Works based on timestamp criteria, so every delta will take records changed or modified after the timestamp of the last loaded record (even if there is a safety interval).
Also One of the main difference is that the CO/FI data sources are "pull based", meaning, that the delta mechanism is based on a time stamp in the source table and data is pulled from these tables into the RSA7 queue.
The LIS* data sources are "push" based meaning, that the delta mechanism is based on a intermediary que to which the delta records are pushed on time of transaction. From the intermediary the delta records are transferred to RSA7 queue. This is done by a R/3 scheduled job independent of BW extractions.
COPA delta works based on timestamp. When the delta infopak is run, the last extraction timestamp is read (from some control tables in source system, BWOM***, i guess) and the data is updated to BW from COPA tebles, CE1****. There will be a safety interval (upper limit) of 30 min, meaning the records posted in the last 30 min will not be loaded. Pull mechanism. When infopak is run records are written to delta queue from copa tables and updated to BW.
LO has a different mechanism of handling delta. The delta records are written to Extraction queue/update queue from the transaction (VA02 for eg.). Then the V3 jobs writes these records to the delta queue. Push mechanism: extractor determines delta. records will be written to the extraction/update queues and then delta queue and wait until the infopak is triggered from BW.
COPA document created during Billing document T code VF01 in SD.
*********************
*********************
